| Cat nr | Stock | Quantity (gr) | Price |
| 256 | In stock | 100 g | €90 |
| 256 | In stock | 500 g | €180 |
| 256 | In stock | 1 kg | €240 |
| 256 | In stock | 5 kg | €510 |
**Pricing disclaimer
Abstract
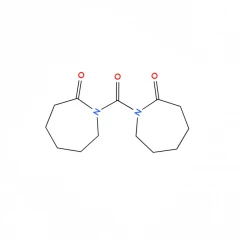
In this chapter the preparation high molecular weight polycondensates is described via chain extension of regular polymers during a reactive processing step, as an alternative route for the solid-state post-condensation (SSP) process. It is shown that carbonyl biscaprolactam (CBC) is a very promising chain extender. Various polymers, such as poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET), poly(butylene terephthalate (PBT), nylon-6 and nylon-6,6 were tested, and in all cases a strong increase of molecular weight was obtained. The viscosity level is controllable by the amount of CBC. The chain extended polymers are strictly linear, according to SEC and rheology measurements. A strict linear chain extension (no chain branching) is important in many applications. Most of the reactive extrusion work is done in the DSM micro-compounder, and some experiments are repeated in a ZSK30 extruder to confirm the results, and to improve the reliability of the translation to commercial equipments. The desired increase in molecular weight is obtained in 1 to 3 minutes, which is an acceptable time span for many applications. The resulting polymers are melt stable, since the chain extension reaction is completed within this residence time.
Publication Carbonyl Bis Caprolactam, used in recycling of PET and PEF.
Loontjens, J. A. (2005). Performance materials by a modular approach Eindhoven: Technische Universiteit Eindhoven DOI: 10.6100/IR594709