- Homepage
- All Products
- Polymers - Biodegradable & Biocompatible
- Chitosan - Cas 9012-76-4
Chitosan - Cas 9012-76-4
Product specifications
Molecular Weight: On request
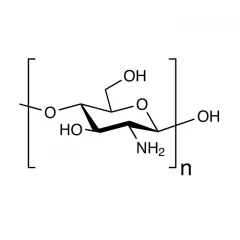
Chemical Formula: (C₆H₁₁NO₄)ₙ
Structure: Composed of β-(1→4)-linked D-glucosamine and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine units.
Solubility:
Soluble in weak acidic solutions (e.g., acetic acid, formic acid).
Insoluble in neutral and alkaline solutions.
pH Sensitivity: Exhibits pH-dependent solubility, making it useful in controlled drug delivery.
Biodegradability: Decomposes into non-toxic, bioactive oligosaccharides in the body or environment.
Degree of Deacetylation (DDA): Typically 50–95%, affecting its solubility and biological activity.
Price & Availability
| Cat nr | Stock | Quantity | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| C1124-100 | Out of stock | 100 g | On request |
| C1124-250 | Out of stock | 250 g | On request |
| C1124-500 | Out of stock | 500 g | On request |
| C1124-1000 | Out of stock | 1 kg | On request |
Chitosan: A Natural Biopolymer with Wide Applications
Chitosan is a biodegradable, biocompatible, and non-toxic polysaccharide derived from chitin, the second most abundant natural polymer after cellulose. It is primarily extracted from the exoskeletons of crustaceans (such as shrimp, crab, and lobster) and fungal cell walls. Due to its unique antimicrobial, film-forming, and bioadhesive properties, chitosan is widely used in biomedical, pharmaceutical, agricultural, environmental, and industrial applications.
Chitosan Production Process
Extraction of Chitin – Obtained from crustacean shells by deproteinization (NaOH) and demineralization (HCl).
Deacetylation of Chitin – Treatment with strong alkali (NaOH) removes acetyl groups, converting it into chitosan.
Purification & Processing – Chitosan is purified, dried, and formulated into powders, hydrogels, films, and nanoparticles.
Biomedical & Pharmaceutical Uses
Wound Healing & Hemostatic Agents
- Accelerates tissue regeneration and prevents infections due to antimicrobial properties.
- Used in bandages, surgical sutures, and burn wound dressings.
Drug Delivery Systems
- pH-sensitive polymer used for controlled drug release.
- Forms nanoparticles, microspheres, and hydrogels for oral, ocular, and transdermal drug delivery.
- Enhances drug absorption and bioavailability.
Tissue Engineering & Implants
- Used in scaffolds for cartilage, bone, and nerve regeneration.
- Supports stem cell growth and bioprinting applications.
Antimicrobial & Antifungal Activity
- Effective against bacteria (E. coli, S. aureus), fungi, and viruses.
Used in dental materials, antibacterial coatings, and medical devices.
Environmental Applications
Water Purification & Heavy Metal Removal
-
- Chitosan binds to heavy metals (Pb²⁺, Cd²⁺, As³⁺) and organic pollutants.
- Used in wastewater treatment and filtration systems.
Biodegradable Packaging & Plastics
-
- Used in eco-friendly films, coatings, and bioplastics as a sustainable alternative to petroleum-based plastics.
Conclusion
Chitosan is a versatile, natural biopolymer with diverse applications in medicine, agriculture, water treatment, and packaging. Its biocompatibility, antimicrobial properties, and ability to form hydrogels and nanoparticles make it an essential biomaterial for future innovations in biomedicine, food preservation, and sustainable materials. As research progresses, chitosan-based technologies are expected to play a significant role in eco-friendly and advanced healthcare solutions.

