- Homepage
- All Products
- Polymers - Biodegradable & Biocompatible
- DL-Lactide - CAS No 95-96-5
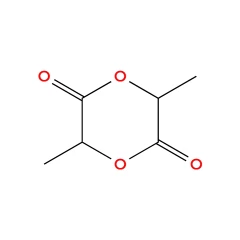
DL-Lactide - CAS No 95-96-5
Product specifications
Purity: >99.5%
Name: L-3,6-Dimethyl-1,4-dioxane-2,5-dione
CAS No: 95-96-5
Appearance: white particle
Molecular Formula: C₆H₈O₄
Molecular Weight: 144.13 g/mol
Appearance: White crystalline solid
Melting Point: ~124–126°C (higher than L-lactide)
Solubility: Soluble in organic solvents like chloroform, acetone, and ethyl acetate; poorly soluble in water.
Price & Availability
| Cat nr | Stock | Quantity | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| J250348-100 | In stock | 100 g | On request |
| J250348-250 | In stock | 250 g | On request |
| J250348-500 | In stock | 500 g | On request |
| J250348-1000 | In stock | 1 kg | On request |
DL-Lactide: A Racemic Form of Lactide for Biodegradable Polymers
DL-Lactide is the racemic (optically inactive) form of lactide, consisting of an equal mixture of D-lactide and L-lactide enantiomers. It is a cyclic dimer of lactic acid and serves as a precursor for polylactic acid (PLA) and other biodegradable polymers.
Synthesis & Production
DL-Lactide is synthesized by the controlled condensation and cyclization of DL-lactic acid, which itself is derived from microbial fermentation or chemical synthesis. Unlike L-lactide, DL-lactide does not exhibit optical activity because it contains an equal proportion of D- and L-lactic acid units.
The polymerization of DL-lactide using ring-opening polymerization (ROP) with metal catalysts (such as tin(II) octoate) produces poly(DL-lactic acid) (PDLLA), which differs from PLA derived from purely L-lactide.
Applications
Biodegradable Polymers (PDLLA)
- Used in drug delivery systems, scaffolds for tissue engineering, and biodegradable packaging.
- Compared to PLLA (poly-L-lactic acid), PDLLA has amorphous properties, making it more flexible and faster degrading.
Biomedical Applications
- PDLLA from DL-lactide is widely used in medical implants, including resorbable sutures, orthopedic screws, and bone fixation devices.
- Used in controlled drug release formulations due to its tunable degradation rate.
Sustainable Plastics
- PDLLA from DL-lactide is an eco-friendly plastic alternative, used in compostable packaging and disposable materials.
Comparison: DL Lactide vs. L-Lactide
| Property | DL-Lactide | L-Lactide |
|---|---|---|
| Optical Activity | Racemic (optically inactive) | Optically active (L-form) |
| Melting Point | Higher (~124–126°C) | Lower (~96–98°C) |
| Polymer Type | Amorphous PDLLA | Crystalline PLLA |
| Mechanical Strength | More flexible, faster degradation | More rigid, slower degradation |
| Biodegradability | Faster | Slower |
Advantages of DL-Lactide
Produces amorphous polymers, making it more suitable for flexible applications.
Faster degradation than PLLA, beneficial for drug delivery and temporary implants.
Retains biocompatibility and biodegradability, making it ideal for medical and environmental applications.
Challenges
Lower mechanical strength compared to PLLA, limiting its use in load-bearing applications.
Higher melting point may affect processing conditions.
Conclusion
DL-Lactide is a crucial monomer for biodegradable and biocompatible polymers, particularly PDLLA, which is widely used in medical, pharmaceutical, and sustainable plastic applications. Its faster degradation rate and amorphous properties make it distinct from L-lactide, allowing for diverse applications in drug delivery, tissue engineering, and biodegradable packaging.

